✅ Method 1: Using the Run Dialog
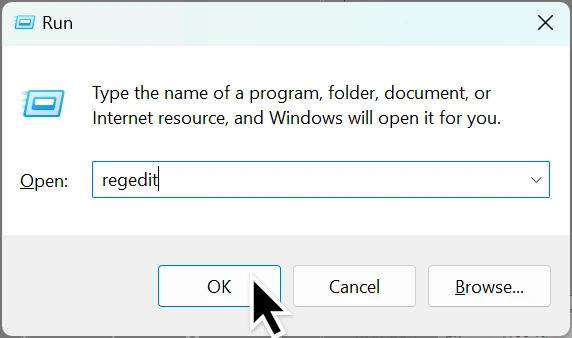
- Press
Windows Key + Ron your keyboard. - Type:
regedit - Click OK or press
Enter.
- If prompted by User Account Control (UAC), click Yes to allow.
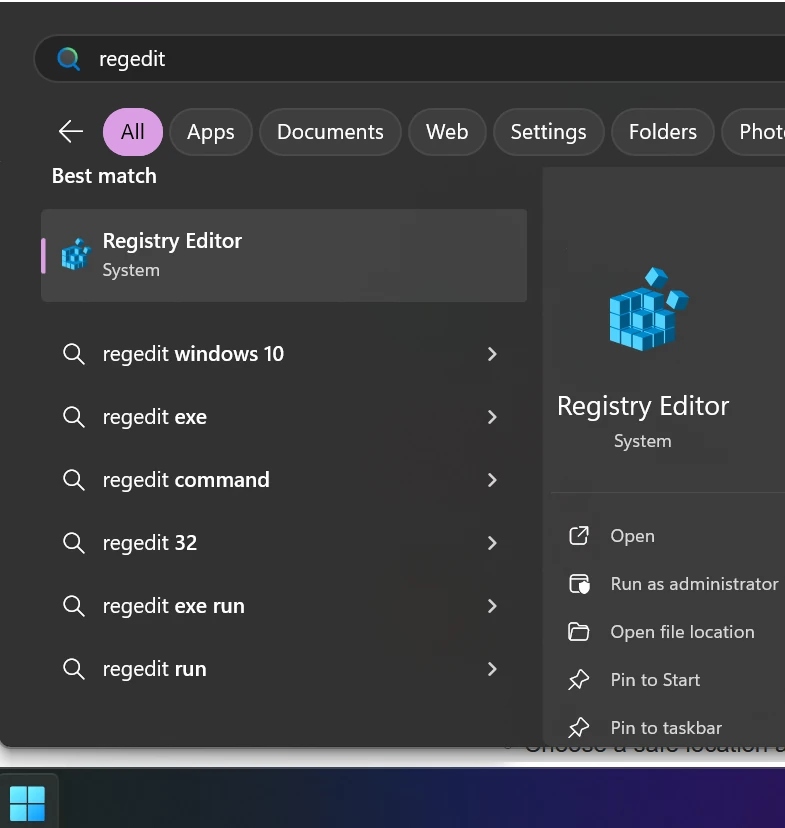
✅ Method 2: Using Windows Search
- Click the Start button or press the
Windowskey. - Type:
regedit - In the search results, click Registry Editor.
- Click Yes if the UAC prompt appears.
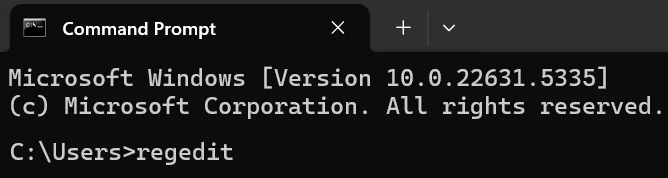
✅ Method 3: Using Command Prompt or PowerShell
- Open Command Prompt or PowerShell.
- Type:
regeditand pressEnter.
🧠 What is the Windows Registry?
The Windows Registry is a hierarchical database that stores settings and configurations for Windows and installed applications.
⚠️ Important Tips Before Editing the Registry
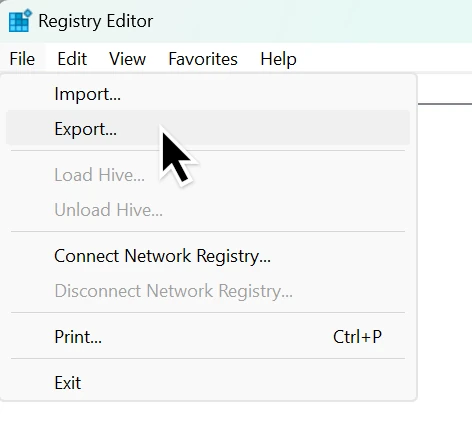
- Always back up the registry before making changes:
- In Registry Editor, click File > Export.
- Choose a safe location and name for the backup file.
- Be cautious: Incorrect changes can cause serious system problems.
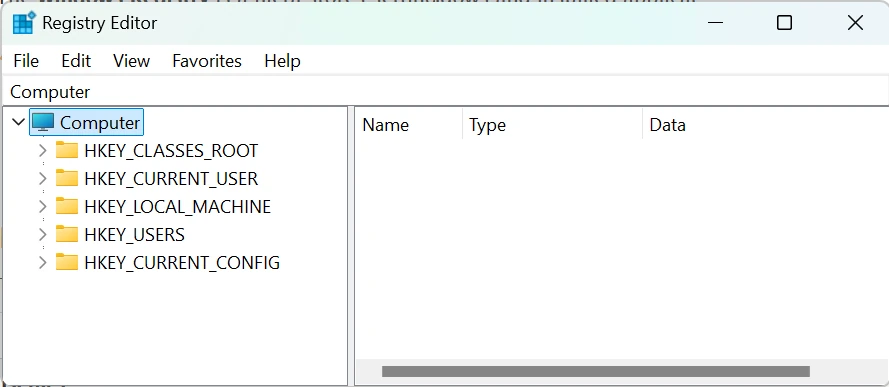
📂 Navigating the Registry
The registry has five main root keys:
HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT(file associations)HKEY_CURRENT_USER(current user settings)HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE(system-wide settings)HKEY_USERS(all user profiles)HKEY_CURRENT_CONFIG(hardware profile info)
Use the left pane to browse, and the right pane to view/edit values.